Good Seller Fast Delivery Wood Bay Againe
The Importance of Timing: Revenue and Expense Recognition
Revenue is recognized when earned and payment is assured; expenses are recognized when incurred and the revenue associated with the expense is recognized.
Learning Objectives
Explain how the timing of expense and acquirement recognition affects the financial statements
Fundamental Takeaways
Central Points
- According to the principle of acquirement recognition, revenues are recognized in the menses earned (buyer and seller have entered into an understanding to transfer assets ) and if they are realized or realizable ( greenbacks payment has been received or drove of payment is reasonably assured).
- The matching principle, part of accrual accounting, requires that expenses be recognized when obligations are (1) incurred (ordinarily when goods are transferred or services rendered), and (2) that they commencement recognized revenues, which were generated from those expenses.
- As long equally the timing of the recognition of revenue and expense falls within the same accounting period, the revenues and expenses are matched and reported on the income statement.
Primal Terms
- incur: To return somebody liable or subject to.
- accrual accounting: refers to the concept of recognizing and reporting revenues when earned and expenses when incurred, regardless of the effect on cash.
- matching principle: An accounting principle related to revenue and expense recognition in accrual bookkeeping.
Revenues and Matching Expenses
According to the principle of revenue recognition, revenues are recognized in the menses when it is earned (buyer and seller accept entered into an agreement to transfer assets) and realized or realizable (cash payment has been received or drove of payment is reasonably assured).
For example, if a company enters into a new trading relationship with a buyer, and it enters into an agreement to sell the buyer some of its goods. The company delivers the products but does not receive payment until thirty days later on the delivery. While the visitor had an agreement with the buyer and followed through on its end of the contract, since there was no pre-existing relationship with the buyer prior to the sale, a conservative auditor might not recognize the revenue from that sale until the company receives payment thirty days later.
Expense Recognition
The assets produced and sold or services rendered to generate acquirement also generate related expenses. Bookkeeping standards require that companies using the accrual basis of bookkeeping and match all expenses with their related revenues for the period, so that the income argument shows the revenues earned and expenses incurred in the right accounting menstruation.
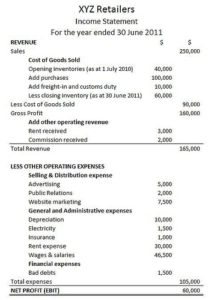
A Sample Income Argument: Expenses are listed on a company's income statement.
The matching principle, office of the accrual accounting method, requires that expenses be recognized when obligations are (1) incurred (unremarkably when goods are transferred, such as when they are sold or services rendered) and (2) the revenues that were generated from those expenses (based on cause and effect) are recognized.
For example, a company makes toy soldiers and acquires wood to brand its goods. It acquires the wood on January ist and pays for it on Jan 15th. The wood is used to make 100 toy soldiers, all of which are sold on February fifteen. While the costs associated with the forest were incurred and paid for during Jan, the expense would not be recognized until February 15th when the soldiers that the forest was used for were sold.
If no crusade-and-effect human relationship exists (e.g., a sale is incommunicable), costs are recognized equally expenses in the accounting menstruation they expired (e.g., when they take been used up or consumed, spoiled, dated, related to the product of substandard appurtenances, or the services are not in need). Examples of costs that are expensed immediately or when used up include administrative costs, R&D, and prepaid service contracts over multiple bookkeeping periods.
The Upshot of Timing on Revenues & Expenses
Often, a business will spend greenbacks on producing their goods earlier information technology is sold or will receive greenbacks for expert sit has not withal delivered. Without the matching principle and the recognition rules, a business would be forced to tape revenues and expenses when it received or paid greenbacks. This could distort a business's income statement and go far wait like they were doing much better or much worse than is really the case. By tying revenues and expenses to the completion of sales and other coin generating tasks, the income argument will better reflect what happened in terms of what revenue and expense generating activities during the accounting menses.
Electric current Guidelines for Revenue Recognition
Transactions that event in the recognition of acquirement include sales assets, services rendered, and revenue from the employ of company assets.
Learning Objectives
Explain how the revenue recognition principle affects how a transaction is recorded
Key Takeaways
Key Points
- Nether accrual accounting, revenues are recognized when they are realized (payment collected) or realizable (the seller has reasonable assurance that payment on goods will be collected) and when they are earned (commonly occurs when appurtenances are transferred or services rendered).
- For companies that don't follow accrual accounting and use the cash -basis instead, revenue is only recognized when cash is received.
- Acquirement recognition is a part of the accrual bookkeeping concept that determines when revenues are recognized in the accounting period.
- The matching principle, forth with revenue recognition, aims to match revenues and expenses in the correct accounting period. It allows a improve evaluation of the income statement, which shows the revenues and expenses for an bookkeeping period or how much was spent to earn the catamenia's revenue.
Key Terms
- fixed nugget: Asset or property which cannot easily be converted into cash, such equally country, buildings, and machinery.
- intangible asset: Whatever valuable belongings of a concern that does not appear on the balance sail, including intellectual property, customer lists, and goodwill.
Acquirement Recognition Concepts
The revenue recognition principle is a cornerstone of accrual accounting together with the matching principle. They both make up one's mind the accounting catamenia in which revenues and expenses are recognized. Co-ordinate to the principle, revenues are recognized if they are realized or realizable (the seller has collected payment or has reasonable assurance that payment on goods will be collected). Revenues must likewise exist earned (usually occurs when appurtenances are transferred or services rendered), regardless of when cash is received. For companies that don't follow accrual accounting and utilize the cash-basis instead, revenue is only recognized when cash is received.
Presentation of Revenue Trends over Time: Guidelines for revenue recognition will bear upon how and when revenue is reported on the income argument.
Transactions that Recognize Revenue
Transactions that result in the recognition of revenue include:
- Sales of inventory, which are typically recognized on the date of sale or engagement of commitment, depending on the shipping terms of the auction
- Sales of avails other than inventory, typically recognized at point of auction.
- Sales of services rendered, recognized when services are completed and billed.
- Revenue from the utilise of the company's assets such as interest earned for money loaned out, hire for using fixed assets, and royalties for using intangible assets, such equally a licensed trademark. Revenue is recognized due to the passage of time or equally avails are used.
The Matching Principle
The matching principle's primary goal is to lucifer revenues and expenses in the right accounting period. The principle allows a better evaluation of the income statement, which shows the revenues and expenses for an bookkeeping period or how much was spent to earn the period'due south revenue. Past following the matching principle, businesses reduce confusion from a mismatch in timing between when costs (expenses) are incurred and when revenue is recognized and realized.
Recognition of Acquirement at Point of Sale or Delivery
Companies can recognize acquirement at point of sale if it is besides the date of delivery or if the buyer takes firsthand ownership of the goods.
Learning Objectives
Explain how the delivery engagement affects acquirement recognition
Key Takeaways
Key Points
- The accrual journal entry to tape the sale involves a debit to the accounts receivable account and a credit to sales revenue; if the auction is for greenbacks, debit cash instead. The revenue earned will be reported as part of sales revenue in the income statement for the current bookkeeping menses.
- When transfer of ownership of goods sold is non immediate and delivery of the goods is required, the shipping terms of the sale dictate when acquirement is recognized. Shipping terms are typically " Pull a fast one on Destination" and "Play tricks Aircraft Point".
- If a company cannot reasonably judge the corporeality of time to come returns and/or has extremely high rates of returns on sales, they should recognize revenues only when the correct of return expires.
Cardinal Terms
- accrual: A charge incurred in i bookkeeping period that has not been paid by the end of information technology.
- Play a trick on: Stands for "Gratuitous on Board" or "Freight on Board"; specifies which party (buyer or seller) pays for shipment and loading costs, and/or where responsibility for the goods is transferred.
Recognizing Acquirement at Point of Sale or Delivery
Goods sold, especially retail goods, typically earn and recognize revenue at point of sale, which can also exist the date of delivery if the heir-apparent takes immediate ownership of the merchandise purchased. Since most sales are made using credit rather than cash, the revenue on the sale is still recognized if collection of payment is reasonably assured. The accrual journal entry to record the sale involves a debit to the accounts receivable account and a credit to the sales acquirement account; if the sale is for cash, the greenbacks account would be debited instead. The acquirement earned volition be reported as part of sales acquirement in the income statement for the current accounting period.

Street Market in Republic of india with Appurtenances for Sale: A street market seller recognizes revenue when he relinquishes his trade to a heir-apparent and receives payment for the particular sold.
Terms of Delivery
When the transfer of ownership of goods sold is not immediate and delivery of the goods is required, the aircraft terms of the auction dictate when revenue is recognized. Shipping terms are typically "Trick Destination" and "FOB Shipping Signal". For goods shipped under FOB destination, ownership passes to the buyer when the goods make it at the buyer's receiving dock; at this point, the seller has completed the sales transaction and revenue has been earned and is recorded. If the shipping terms are FOB aircraft signal, ownership passes to the buyer when the goods go out the seller'southward shipping dock, thus the auction of the appurtenances is consummate and the seller can recognize the earned revenue.
Revenue Recognition & Right of Render
If a company cannot reasonably estimate the amount of future returns and/or has extremely high rates of returns on sales, they should recognize revenues only when the correct of return expires. Those companies that can estimate the number of future returns and have a relatively pocket-size return rate tin can recognize revenues at the point of sale, but must deduct estimated future returns.
Recognition of Revenue Prior to Commitment
Accrual accounting allows some revenue recognition methods that recognize revenue prior to delivery or sale of goods.
Learning Objectives
Distinguish betwixt the percentage of completion method and the completion of production method of acquirement recognition
Primal Takeaways
Key Points
- For most goods that have been sold and are undelivered, the sales transaction is not complete and revenue on the sale has non been earned. In this instance, an accrual entry for revenue on the sale is not made.
- The cash method of accounting recognizes acquirement and expenses when cash is exchanged. For a seller using the cash method, if greenbacks is received prior to the delivery of goods, the cash is recorded as earnings.
- Under the pct-of-completion method, if a long-term contract specifies the price and payment options with transfer of ownership and details the buyer's and seller's expectations, then revenues, costs, and gross profit can be recognized each period based upon the progress of construction.
- The completion of production method allows recognizing revenues fifty-fifty if no sale was made. This applies to natural resources where there is a gear up marketplace for these products with reasonably assured prices, units are interchangeable, and selling and distributing costs are not significant.
Key Terms
- conservatism: A risk-balky attitude or approach; for accounting purposes, it relates to disclosing expenses and losses incurred immediately and delaying the recognition of revenues and gains until realized.
- accrual: A charge incurred in ane accounting period that has not been paid by the end of it.
Definition of Revenue Recognition
The accounting principle regarding revenue recognition states that revenues are recognized when they are earned (transfer of value between heir-apparent and seller has occurred) and realized or realizable (collection is reasonably bodacious). A transfer of value takes place between a heir-apparent and seller when the buyer receives goods in accordance to a sales social club approved by the buyer and seller and the seller receives payment or a hope to pay from the buyer for the goods purchased. Acquirement must be realizable. In guild words, for sales where cash was not received, the seller should be confident that the buyer will pay according to the terms of the sale.

Appurtenances in Inventory: Depending on the shipping terms of the sale, a seller may not recognize revenue on appurtenances sold that are pending delivery.
Methods that Recognize Revenue Prior to Commitment or Sale
- Percentage-of-completion method: if a long-term contract clearly specifies the price and payment options with transfer of ownership -- the buyer is expected to pay the whole amount and the seller is expected to complete the project -- then revenues, expenses, and gross profit tin can be recognized each period based upon the progress of construction (that is, percentage of completion). For instance, if during the twelvemonth, 25% of the edifice was completed, the builder can recognize 25% of the expected total profit on the contract. Per centum of completion is preferred over the completed contract method. However, expected loss should exist recognized fully and immediately due to the conservatism constraint. All revenues, expenses, losses, and gains resulting from the percentage completed volition be reported on the income statement.
- Completion of production method: This method allows recognizing revenues fifty-fifty if no sale was fabricated. This applies to agricultural products and minerals because there is a prepare market for these products with reasonably assured prices, the units are interchangeable, and selling and distributing does not involve significant costs. All expected revenues and costs of product related to the units produced will exist reported on the income statement.
Recognition of Revenue After Delivery
At that place are three methods that recognize revenue afterwards delivery has taken place: the installment sales, cost recovery, and deposit methods.
Learning Objectives
Differentiate between the installment sales method, the toll recover method and the eolith method to account for recognizing acquirement subsequently the delivery of goods
Fundamental Takeaways
Key Points
- When a auction of goods carries a high dubiousness on collectibility, a company must defer the recognition of acquirement until after delivery.
- The installment sales method recognizes income later on a sale or delivery is made; the acquirement recognized is a proportion or the product of the percent of acquirement earned and greenbacks collected.
- The price recovery method is used when there is an extremely loftier probability of uncollectable payments. Under this method, no revenue is recognized until cash collections exceed the seller's cost of the merchandise sold.
- The eolith method is used when a company receives cash before transfer of ownership occurs. Revenue is non recognized when cash is received, because the risks and rewards of ownership have not transferred to the buyer. Only as the transfer of value takes place is revenue recognized.
Key Terms
- deferral: An account where the asset or liability recording cash paid or received is not realized until a time to come engagement (accounting period)
- liability: An obligation, debt or responsibleness owed to someone.
Recognizing Revenue after Delivery of Goods
When a sale of goods transaction carries a loftier degree of incertitude regarding collectibility, a company must defer the recognition of revenue. In this situation, revenue is not recognized at point of sale or delivery. There are three methods that recognize revenue after delivery has taken place:.

Service Commitment: Delivery of goods or service may not be enough to let for a business organization to recognize revenue on a sale if there is dubiety that the customer will pay what it owes.
The installment sales method recognizes income after a sale or delivery is made; the revenue recognized is a proportion or the production of the percent of revenue earned and greenbacks collected. The unearned income is deferred (recorded as a liability ) and and then recognized to income when cash is collected. For example, if a visitor collected 45% of a product's sale price, it can recognize 45% of total acquirement on that product. The installment sales method is typically used to account for sales of consumer durables, retail state sales, and retirement property.
The cost recovery method is used when there is an extremely high probability of uncollectable payments. Under this method, no revenue is recognized until greenbacks collections exceed the seller's toll of the merchandise sold. For instance, if a visitor sold a machine worth $ten,000 for $15,000, it can kickoff recognizing acquirement when the heir-apparent has made payments in excess of $ten,000. In other words, each dollar collected greater than $ten,000 goes towards the seller's predictable revenue on the sale of $5,000.
The deposit method is used when a company receives cash before transfer of buying occurs. Revenue is not recognized when cash is received because the risks and rewards of ownership take non transferred to the buyer. The seller records the cash deposit equally a deferred revenue, which is reported equally a liability on the balance sheet until the revenue is earned. For case, sales of magazine subscriptions employ the eolith method to recognize revenue. A deferral is recorded when a seller receives a subscriber's payment on the subscription; cash is debited and deferred mag subscriptions (a liability account) is credited. As the delivery of the magazines take place, a portion of revenue is recognized, and the deferred liability account is reduced for the amount of the revenue.
Differences Betwixt Accrual-Basis and Cash-Basis Accounting
Accrual accounting does not record revenues and expenses based on the substitution of cash, while the cash-basis method does.
Learning Objectives
Differentiate between accrual and cash ground accounting
Key Takeaways
Central Points
- Accrual accounting does not consider greenbacks when recording revenue; in near cases, goods must exist transferred to the buyer in order to recognize earnings on the auction. An accrual periodical entry is made to record the revenue on the transferred goods equally long as drove of payment is expected.
- In accrual accounting, expenses incurred in the same menses that revenues are earned are also accrued for with a journal entry. Same equally revenues, the recording of the expense is unrelated to the payment of cash.
- For a seller using the cash method, revenue on the auction is not recognized until payment is nerveless and expenses are non recorded until cash is paid.
- The cash model is only acceptable for smaller businesses for which a majority of transactions occur in cash and the utilize of credit is minimal.
Cardinal Terms
- accrue: To increment, to augment; to come to by manner of increase; to arise or spring equally a growth or result; to exist added equally increase, profit, or damage, specially as the produce of money lent.
- liability: An obligation, debt or responsibleness owed to someone.
Definition of Accrual Accounting
Under the accrual bookkeeping method, the receipt of cash is not considered when recording revenue; notwithstanding, in most cases, goods must be transferred to the buyer in lodge to recognize earnings on the auction. An accrual journal entry is made to tape the revenue on the transferred goods even if payment has non been made. If goods are sold and remain undelivered, the sales transaction is not consummate and revenue on the sale has not been earned. In this case, an accrual entry for acquirement on the auction is not fabricated until the appurtenances are delivered or are in transit. Expenses incurred in the aforementioned period in which revenues are earned are also accrued for with a journal entry. Just like revenues, the recording of the expense is unrelated to the payment of greenbacks. An expense account is debited and a cash or liability account is credited.
Definition of Cash-Basis Bookkeeping
The cash method of accounting recognizes revenue and expenses when cash is exchanged. For a seller using the greenbacks method, revenue on the sale is not recognized until payment is collected. Just like revenues, expenses are recognized and recorded when cash is paid. The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB), which dictates accounting standards for most companies—peculiarly publicly traded companies—discourages businesses from using the cash model because revenues and expenses are not properly matched. The greenbacks model is adequate for smaller businesses for which a majority of transactions occur in cash and the utilise of credit is minimal. For example, a mural gardener with clients that pay by cash or check could use the cash method to account for her concern' transactions.

A cashier at a hotel in Thailand: The cash-basis method, unlike the accrual method, relies on the receipt and payment of cash to recognize revenues and expenses.
Licenses and Attributions
CC licensed content, Shared previously
- Curation and Revision. Provided past: Boundless.com. License: CC Past-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
CC licensed content, Specific attribution
- Deferral. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deferral. License: CC By-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Matching principle. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Matching_principle. License: CC By-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Accrual basis accounting. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Accrual_basis_accounting. License: CC Past-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Boundless. Provided past: Boundless Learning. Located at: http://world wide web.dizzying.com//finance/definition/matching-principle. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- incur. Provided by: Wiktionary. Located at: http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/incur. License: CC By-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Boundless. Provided by: Boundless Learning. Located at: http://www.boundless.com//accounting/definition/accrual-accounting. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- All sizes | y2cary3n6mng-5ha51l-income-statement-instance | Flickr - Photo Sharing!. Provided by: Flickr. Located at: http://www.flickr.com/photos/sampjb/7690678408/sizes/fifty/. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- fixed asset. Provided by: Wiktionary. Located at: http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/fixed_asset. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- intangible asset. Provided by: Wiktionary. Located at: http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/intangible_asset. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Matching principle. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Matching_principle. License: CC By-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Acquirement recognition. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Revenue_recognition. License: CC Past-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- All sizes | y2cary3n6mng-5ha51l-income-argument-case | Flickr - Photo Sharing!. Provided by: Flickr. Located at: http://www.flickr.com/photos/sampjb/7690678408/sizes/l/. License: CC Past-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Missouri Revenue suffered in 2009 | Flickr - Photo Sharing!. Provided by: Flickr. Located at: http://www.flickr.com/photos/hotflashblogger/4341243331/. License: CC By: Attribution
- Income statement. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Income_statement. License: CC Past-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Revenue recognition. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Revenue_recognition. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Accrual ground accounting. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Accrual_basis_accounting. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- FOB (shipping). Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FOB_(shipping). License: CC By-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- accrual. Provided by: Wiktionary. Located at: http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/accrual. License: CC By-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Boundless. Provided by: Boundless Learning. Located at: http://www.boundless.com//accounting/definition/fox. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- All sizes | y2cary3n6mng-5ha51l-income-statement-example | Flickr - Photo Sharing!. Provided by: Flickr. Located at: http://www.flickr.com/photos/sampjb/7690678408/sizes/l/. License: CC Past-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Missouri Revenue suffered in 2009 | Flickr - Photograph Sharing!. Provided by: Flickr. Located at: http://www.flickr.com/photos/hotflashblogger/4341243331/. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Goods for sale, Calangute beach, Goa, India | Flickr - Photo Sharing!. Provided by: Flickr. Located at: http://www.flickr.com/photos/paulmannix/464063059/. License: CC By: Attribution
- accrual. Provided by: Wiktionary. Located at: http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/accrual. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Deferral. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deferral. License: CC By-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Income argument. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Income_statement. License: CC Past-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Revenue recognition. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Revenue_recognition. License: CC By-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- conservatism. Provided by: Wiktionary. Located at: http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/conservatism. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- All sizes | y2cary3n6mng-5ha51l-income-statement-example | Flickr - Photo Sharing!. Provided by: Flickr. Located at: http://www.flickr.com/photos/sampjb/7690678408/sizes/l/. License: CC By-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Missouri Revenue suffered in 2009 | Flickr - Photo Sharing!. Provided by: Flickr. Located at: http://www.flickr.com/photos/hotflashblogger/4341243331/. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Goods for sale, Calangute embankment, Goa, India | Flickr - Photograph Sharing!. Provided by: Flickr. Located at: http://world wide web.flickr.com/photos/paulmannix/464063059/. License: CC BY: Attribution
- 20111020-FNS-LSC-0063 | Flickr - Photo Sharing!. Provided by: Flickr. Located at: http://www.flickr.com/photos/usdagov/6629278631/. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Deferral. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deferral. License: CC Past-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Revenue recognition. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Revenue_recognition. License: CC By-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Installment sales method. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Installment_sales_method. License: CC By-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Income argument. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Income_statement. License: CC By-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Deferred income. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deferred_income. License: CC Past-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- deferral. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/deferral. License: CC Past-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- liability. Provided by: Wiktionary. Located at: http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/liability. License: CC By-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- All sizes | y2cary3n6mng-5ha51l-income-statement-example | Flickr - Photo Sharing!. Provided by: Flickr. Located at: http://world wide web.flickr.com/photos/sampjb/7690678408/sizes/l/. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Missouri Revenue suffered in 2009 | Flickr - Photo Sharing!. Provided past: Flickr. Located at: http://www.flickr.com/photos/hotflashblogger/4341243331/. License: CC Past: Attribution
- Goods for sale, Calangute embankment, Goa, Bharat | Flickr - Photo Sharing!. Provided past: Flickr. Located at: http://www.flickr.com/photos/paulmannix/464063059/. License: CC BY: Attribution
- 20111020-FNS-LSC-0063 | Flickr - Photograph Sharing!. Provided by: Flickr. Located at: http://www.flickr.com/photos/usdagov/6629278631/. License: CC BY: Attribution
- All sizes | Technical Services 16 | Flickr - Photograph Sharing!. Provided by: Flickr. Located at: http://www.flickr.com/photos/sanjoselibrary/5077983155/sizes/50/. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Cash method of bookkeeping. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cash_method_of_accounting. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Bookkeeping methods. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Accounting_methods%23Accrual_basis. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Accrual. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Accrual%23Accruals_in_accounting. License: CC Past-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- accrue. Provided by: Wiktionary. Located at: http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/accumulate. License: CC By-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- liability. Provided by: Wiktionary. Located at: http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/liability. License: CC By-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- All sizes | y2cary3n6mng-5ha51l-income-statement-example | Flickr - Photo Sharing!. Provided by: Flickr. Located at: http://www.flickr.com/photos/sampjb/7690678408/sizes/50/. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Missouri Revenue suffered in 2009 | Flickr - Photo Sharing!. Provided by: Flickr. Located at: http://www.flickr.com/photos/hotflashblogger/4341243331/. License: CC By: Attribution
- Appurtenances for sale, Calangute embankment, Goa, India | Flickr - Photo Sharing!. Provided by: Flickr. Located at: http://world wide web.flickr.com/photos/paulmannix/464063059/. License: CC Past: Attribution
- 20111020-FNS-LSC-0063 | Flickr - Photo Sharing!. Provided by: Flickr. Located at: http://world wide web.flickr.com/photos/usdagov/6629278631/. License: CC BY: Attribution
- All sizes | Technical Services xvi | Flickr - Photo Sharing!. Provided past: Flickr. Located at: http://world wide web.flickr.com/photos/sanjoselibrary/5077983155/sizes/l/. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Cashier | Flickr - Photo Sharing!. Provided by: Flickr. Located at: http://www.flickr.com/photos/stefanedberg62/2406508840/. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
worshamhamered1992.blogspot.com
Source: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-accounting/chapter/revenue-recognition/
0 Response to "Good Seller Fast Delivery Wood Bay Againe"
Postar um comentário